Three Tips to Protect Your Knees From Arthritis
Knee arthritis is one of the most common forms of osteoarthritis.
Knee arthritis accounts for more than 80% of all osteoarthritis and impacts at least 19% of Americans over the age of 45.
For many, a diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis leads to chronic, debilitating knee pain that stops them from doing all of their favorite activities. Sometimes it’s simply due to the limiting belief that once you have arthritis – you’ve got “bad knees” for life.
Other times it’s because you’ve been told you have “bone on bone” in your knee and there’s nothing you can do – except to scale back on activity so that you don’t make it worse. This line of thinking is flawed and often leads people to unnecessary procedures and surgery. One of the best things you can do to protect your knees from the debilitating effects of arthritis is to keep moving.
Here are three tips to help you protect your knees from arthritis as you age – so that you can keep doing all of your favorite activities and avoid any major procedures or surgery:
1. Strengthen Your Hips and Core
Your knee joint is situated just below your hips and core. And research has shown that when you have poor control of your upper leg muscles – you get more stress through your knee joint.
The strength of your upper leg muscles is very much dependent on your hip and core strength. Your thigh bone – or femur – connects your knee and your pelvis – and your core strength controls your pelvis.
If your pelvis isn’t stable – your femur is going to have a difficult time staying in alignment – which will ultimately have an impact on your knee joint. If you’ve got arthritis in your knees, it’s critical you minimize any added stress to your knee joints.
Strengthening your core and having good hip strength is going to help prevent and minimize the symptoms of arthritis and keep you doing activities you love longer.
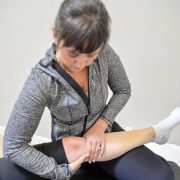
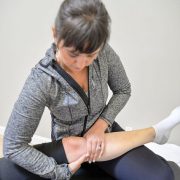
2. Keep Your Knees Mobile
Mobility before stability is my mantra.
And I say this for just about every joint in your body. But it’s especially true for your knees. There are joints whose primary function is stability – and there are those whose major function is mobility.
Your knee needs to be mobile.
Its major purpose is to bend all the way so you can squat and pick things up – and it needs to straighten all the way to give you stability when you need it. When either of these motions are lacking – your ligaments and surrounding muscles will suffer.
A lot of folks just “accept” that their knees are stiff – especially if you’ve been told you have arthritis in your knees. The limiting belief is that stiffness is par for the course. But the truth is that if you keep your knees mobile as you age – you can not only maintain the mobility you have but improve what is lacking.
If your knees are stiff – start moving them. The thing to understand about arthritis is that it’s a normal part of aging. Debilitating mobility is not. Even a 10% improvement in your knee mobility – which can happen even if you’ve got arthritis – will result in huge improvements in your knee function.
It can be the difference between a natural solution to knee pain vs undergoing a major surgery like knee replacement.
3. Don’t Stop Your Activities
When people find out they have arthritis – and especially if they’re in pain – they often think that slowing down or stopping activity will help protect their knees.
This couldn’t be farther from the truth.
Study after study – including one from the Center for Disease Control – shows that severe joint pain among adults with arthritis is worse with inactivity. When you remain active, you keep blood flowing, your knee joints mobile, and your muscles strong. These are very important factors in managing your arthritis. Sometimes, the knee pain you feel when you’re doing certain activities has nothing to do with your arthritis. Statistics show that only 15% of patients with evidence of knee osteoarthritis on X-ray even had symptoms.
That means that the other 85% is walking, biking, and running around enjoying their most favorite activities – despite the fact their X-ray showed arthritis too. The point here is to keep doing your activities – whether you’ve got arthritis already or not – it’s one of the best ways to prevent and protect your knee joints as you age.
So – to review…
If you want to optimize your knee health as you age – which you still can even if you’ve been told you have “advanced arthritis” – prioritize your core strength, the mobility of your knees, and stay active.
Focusing on these three things can have a significant impact on how arthritis affects you – and can help you avoid major (often unnecessary) surgery in your future.
Is knee pain keeping you from doing your favorite activities? Are you considering a major procedure or surgery but not sure if you need it?
Join us on Tuesday Oct. 25th from 6-7pm for our Free Masterclass for Knee Pain Sufferers.
Sign up using this link —> Knee Pain Masterclass.
We hope to see you there!
Can’t make it live? All participants will receive a complimentary replay of the class 🙂
Dr. Carrie Jose, Physical Therapist and Pilates expert, owns CJ Physical Therapy & Pilates in Portsmouth and writes for Seacoast Media Group. To request a free copy of her Knee Pain Free Report CLICK HERE or to get in touch, email her at [email protected].