The Top Four Benefits of Orthopedic Dry Needling and Why You Should Consider it.
Orthopedic dry needling is a modern therapeutic treatment technique that has been adopted by physical therapists and medical professionals to alleviate pain and improve muscle function. But despite its escalating popularity, I’m still surprised at how many people are unaware it even exists.
What exactly is orthopedic dry needling?
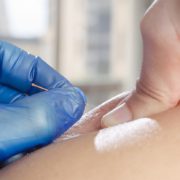
Orthopedic dry needling involves the insertion of fine, sterile acupuncture needles into myofascial trigger points (“knots”), tendons, or muscles that are typically painful, stiff, or causing discomfort. Unlike acupuncture, which aims to balance and restore the flow of energy (“chi”) in your body, dry needling focuses on restoring your muscles and soft tissue back to their optimal state. During a dry needling treatment, a needle is inserted into specific areas to encourage blood flow and homeostasis, sometimes eliciting a ‘twitch’ response in the muscles. The needles may remain in place for a short duration, or may be removed quickly, depending on the condition being treated. Dry needling is backed by scientific research and has been shown to work effectively. It’s thought to turn off trigger points, ease muscle tension, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain – all to help improve how your muscles perform and work.
Here are the top 4 benefits of orthopedic dry needling and why you should consider this treatment technique if you haven’t already:
1. Pain Relief
Dry needling can quickly alleviate pain, which means you can get back to your regular activities sooner. While the treatment itself can sometimes be painful, and lead to residual soreness 24-48 hours after your treatment, you’ll find that the positives far outweigh the negatives. Most of my clients find that a little bit of soreness right after the treatment is well worth the pain relief they experience afterwards. Dry needling works best for pain relief when it’s performed alongside functional and integrative therapies such as corrective movement strategies – which will result in long-lasting pain relief instead of more short-term.
2. Better Mobility
Dry needling does more than just relieve pain – it helps to enhance how you move. When muscles are tight, they can restrict movement and create a lot of discomfort. By releasing tension in tight muscles, increasing blood flow, and reducing inflammation – dry needling facilitates more comfortable and more extensive range motion in your joints. This allows you to move more freely and perform your favorite activities with less pain and restriction. In conjunction with corrective exercises and stretches, dry needling can be an extremely valuable tool for enhancing and maintaining good mobility.
3. Enhanced Muscle Function
Good mobility is just one aspect required for optimal muscle function. Your muscles also need to know how to activate properly and together. Sometimes – when you’ve been suffering from pain for a while – the muscles surrounding the problem area can “fall asleep at the wheel”. While you may be able to successfully get rid of your pain in a particular area, getting rid of and correcting the problem is a different story. I often say: “just because your pain is gone – does not mean your problem is gone”. If you don’t address underlying muscular compensations, your pain will eventually come back and sometimes it’s worse. The stimulation provided by orthopedic dry needling can help get your brain to pay more attention to the affected area, thus, helping “sleepy” muscles come back to the party and work like they’re supposed to.
4. Faster Recovery
When you’re injured, your body needs all the help it can get to heal. Dry needling not only enhances blood flow to the targeted area, but helps to create an environment for muscle regeneration as well – thus – helping to speed up the recovery process of injured or damaged soft tissue. Additionally, the improved blood flow aids in the removal of metabolic waste products and the delivery of nutrients to the tissues, fostering faster healing of the injured areas and less inflammation. This accelerated recovery is particularly valuable for athletes or weekend warriors aiming to return to their sport faster, as well as anyone looking to get back to their favorite activities as quickly as possible.
Should you consider orthopedic dry needling?
When I think of orthopedic dry needling, I think of it like a helping hand to feel better, move more freely, and enhance just about any other treatment you’re using alongside it. For example, a corrective exercise is only going to work if you can execute it properly. If you’ve got stiff, painful muscles that prevent you from performing your exercise or stretch that you know you need to do to help a particular problem – dry needling can be the magic in between.
It’s important to note that dry needling is not necessary or right for everyone. So it’s important that you know what it is and when it can be used to improve your health. If after reading this article you think orthopedic dry needling could be something that you’re missing – talk to a qualified physical therapist or health care practitioner who practices dry needling – and ask if you’re a good fit for this treatment technique.
Dr. Carrie Jose, Physical Therapist and Pilates expert, owns CJ Physical Therapy & Pilates in Portsmouth and writes for Seacoast Media Group. To get in touch, email her at [email protected].